Projects
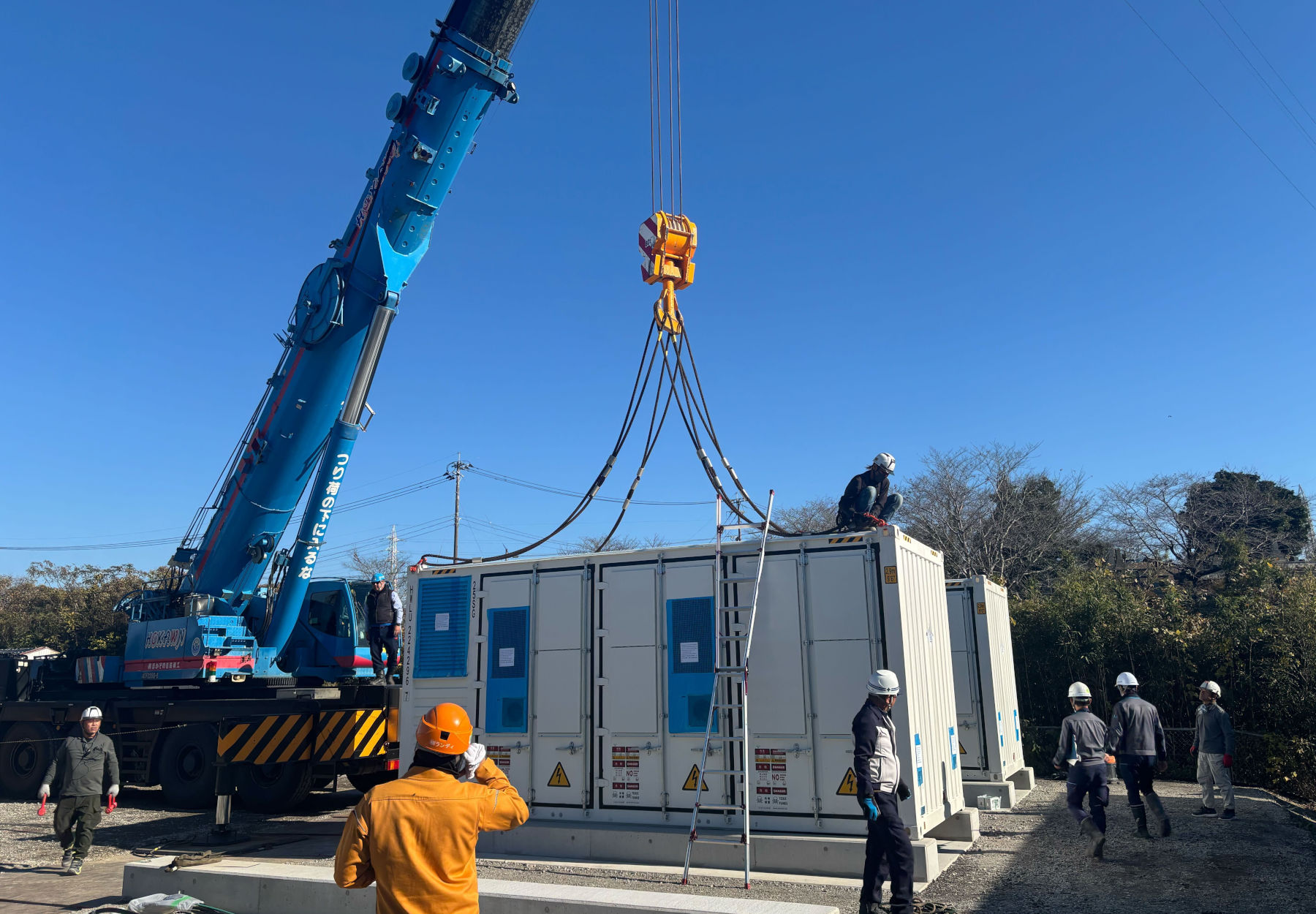
Japan's energy sector is undergoing rapid transformation, driven by decarbonisation targets, renewable energy integration, and grid modernisation. Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) at both Extra High Voltage (EHV, typically 154kV and above) and High Voltage (HV, typically 6.6kV–66kV) levels are increasingly critical for grid stability, frequency regulation, and renewable energy smoothing.
EHV BESS
Typically utility-scale projects (10MW–100MW+), often co-located with renewable plants or at transmission substations. Key players include major utilities (TEPCO, KEPCO), trading houses, and international developers.
HV BESS
Mid-scale systems (1MW–10MW), deployed at distribution substations, industrial sites, and for community energy projects. These support local grid balancing and behind-the-meter applications.
The EHV and HV BESS markets in Japan are expected to grow significantly through 2030, underpinned by renewable energy targets, grid modernisation, and supportive policy frameworks. Strategic locations include Hokkaido, Tohoku, and Kyushu, where renewable penetration is highest and grid constraints are most acute.